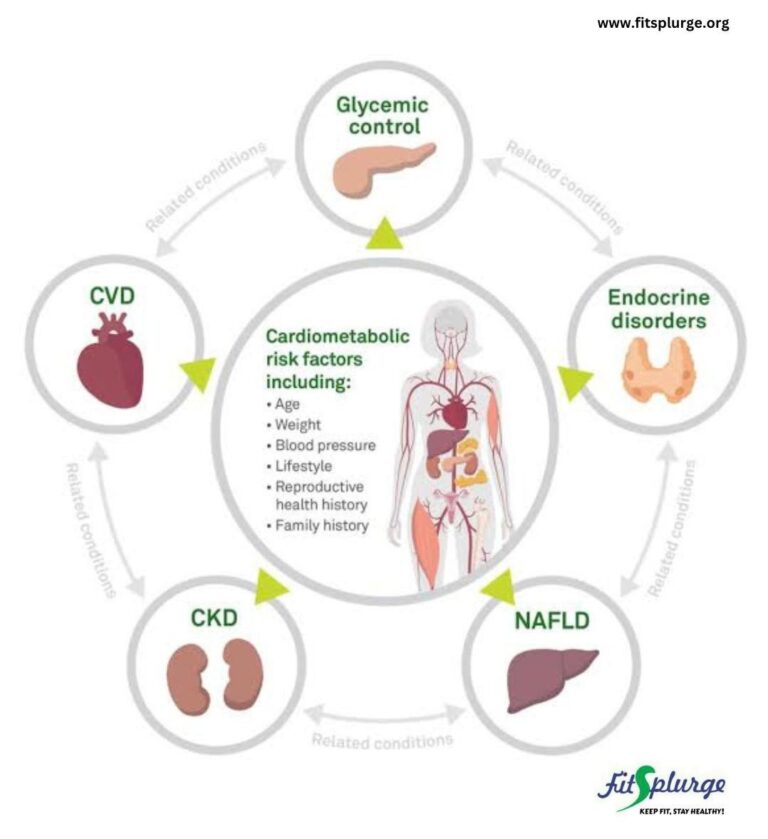
Cardio-metabolic syndrome is a cluster of factors that increase a person’s risk for a heart attack, stroke, and diabetes. These diseases are silent killers but are very preventable. These cluster of risk factors include; high blood pressure, high levels of sugar in the blood, abdominal obesity, and abnormal cholesterol levels.
They contribute to the development of cardiovascular diseases, cerebrovascular diseases, kidney diseases, diabetes, liver diseases, sleep disorders, some cancers, and musculoskeletal issues like arthritis, to mention but a few.
Fortunately, millions of people worldwide are becoming aware of these risk factors and are learning to choose measures that help prevent and manage them. However, with the high prevalence of preventable non-communicable diseases, efforts need to be heightened to increase the awareness of these risk factors
Factors that increase the likelihood of developing the cardiometabolic syndrome include:
Age:
The risk for cardiometabolic syndrome increases with age.
Family History:
Genetics plays a role, particularly if there’s a history of heart disease or diabetes, but a person’s lifestyle mainly triggers the genetic components.
Obesity:
Especially abdominal obesity (fat around the belly) is a huge risk factor.
Sedentary Lifestyle:
Lack of physical activity contributes significantly.
Poor food choices:
High intake of junk foods, processed foods, sodium, sugars, and fats contributes significantly.
Reproductive health history:
For women, the number of children, frequency of conception, history of abortion, and miscarriages are associated with a significant risk of cardiometabolic disease.
Diagnosing the Cardio-Metabolic Syndrome:
With the presence of at least three of the risk factors, the cardiometabolic syndrome can be diagnosed
Preventing the Cardio-Metabolic Syndrome:
Lifestyle factors play a crucial role in the different levels of prevention and management of cardiometabolic syndrome.
Key lifestyle changes to reduce the risk include:
Healthy eating:
A balanced, nutrient-dense diet is important. This includes consuming fruits, vegetables, whole grains, lean proteins, and healthy fats (like those from nuts, seeds, and fish). Reducing the intake of processed foods, added sugars, and unhealthy fats (trans fats, saturated fats) should be prioritized
Physical activity:
Regular exercise (at least 150 minutes of moderate-intensity activity per week) can improve cardiovascular health, lower blood sugar levels, reduce abdominal fat, and enhance good cholesterol levels.
Weight management:
Maintaining a healthy weight, particularly by reducing abdominal obesity can significantly reduce the risk.
Stress management:
Chronic stress can worsen cardiovascular risk factors like blood pressure and blood sugar levels. Avoiding stressors and opting for relaxation techniques such as mindfulness, meditation, yoga, and deep breathing exercises can help.
Good sleep hygiene:
Getting enough restful sleep (7-9 hours per night) is crucial for regulating blood pressure, blood sugar, and overall metabolic health.
Smoking cessation:
Smoking increases the risk of heart disease, stroke, and insulin resistance. Quitting smoking can greatly improve overall health.
Regular Health Checkups: Regular checks for blood pressure, cholesterol, blood sugar, and weight are essential, especially if someone already has the risk factors.
By adopting a healthy lifestyle, individuals can reduce the likelihood of developing cardiometabolic syndrome or manage the conditions if already diagnosed.
Do you have any of these risk factors?
You can speak to one of our health experts about your symptoms
Contact us today
Fitsplurge Cares!
Remember to sign up for our newsletter for more informative articles like this.